Page 69 - Virtual Vascular Vol 4
P. 69
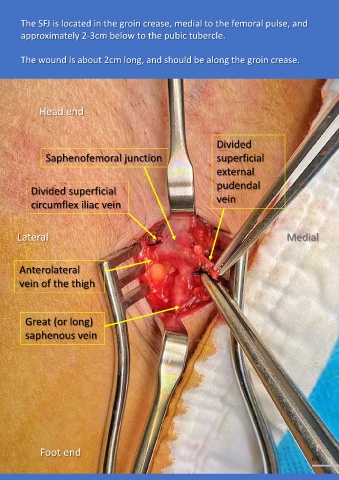
Surgery for Varicose Veins The SFJ is located in the groin crease, medial to the femoral pulse, and
approximately 2-3cm below to the pubic tubercle.
The wound is about 2cm long, and should be along the groin crease.
Indications for treatment of varicose veins:
- worsening symptoms with significant impact on quality of life
- complications of varicose veins such as eczema, skin changes with
hemosiderin pigmentation, lipodermatosclerosis, ulceration. Head end
- bleeding
- Superficial thrombophlebitis with thrombus very near to the
saphenofemoral junction (SFJ), in fear of progression to femoral vein Divided
deep vein thrombosis Saphenofemoral junction superficial
external
SFJ ligation, strip of great saphenous vein (GSV) , and multiple avulsions pudendal
of varicosities (Trendelenburg operation) remain the gold standard of Divided superficial vein
treatment for patients with incompetent SFJ and GSV. Other treatment circumflex iliac vein
options include radiofrequency ablation, laser ablation, or endovenous
cyanoacrylate injection. Lateral Medial
Anterolateral
vein of the thigh
Great (or long)
Usually, there are 5 venous tributaries which join the GSV
before the SFJ at the fossa ovalis. These 5 tributaries saphenous vein
should all be ligated individually and divided at surgery to
minimize the chance of recurrence.
Can you name these tributaries?
Foot end
68 69