Page 9 - Virtual Vascular Vol 3
P. 9
Radiocephalic AV fistula creation at
the anatomical snuffbox
An Arteriovenous fistula is created between a superficial artery (radial artery) and a
superficial vein (cephalic vein) to create a high flow superficial conduit for hemodialysis
access.
The anatomical snuffbox (also known as the radial fossa), is a triangular depression
found on the lateral aspect of the dorsum of the hand. It is located at the level of the
carpal bones, and best seen when the thumb is extended.
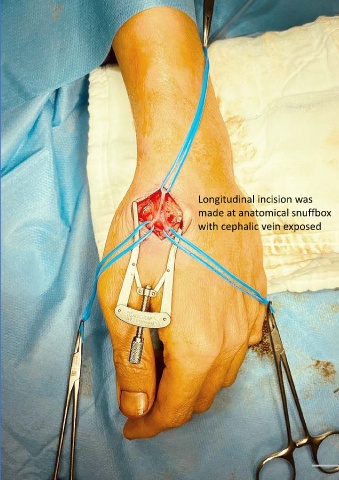
Borders Longitudinal incision was
As the snuffbox is triangularly shaped, it has three borders, a floor, and a roof made at anatomical snuffbox
- Ulnar (medial) border: Tendon of the extensor pollicis longus. with cephalic vein exposed
- Radial (lateral) border: Tendons of the extensor pollicis brevis and abductor pollicis
longus.
- Proximal border: Styloid process of the radius
- Floor: Carpal bones; scaphoid and trapezium
- Roof: Skin.
Contents
The main contents of the anatomical snuffbox are the radial artery, a branch of the
radial nerve, and the cephalic vein:
Radial artery : crosses the floor of the anatomical snuffbox, then turns medially and
travels between the heads of the adductor pollicis muscle. The radial pulse can be
palpated in some individuals by placing two fingers on the proximal portion of the
anatomical snuffbox.
Superficial branch of the radial nerve: found in the skin and subcutaneous tissue of the
anatomical snuffbox. It innervates the dorsal surface of the lateral three and half digits,
and the associated area on the back of the hand.
- Cephalic vein – arises from the dorsal venous network of the hand and crosses the
anatomical snuffbox to travel up the anterolateral aspect of the forearm.
8 9