Page 47 - Virtual Vascular Vol 21
P. 47
The coeliac axis arises anteriorly from
abdominal aorta just below diaphragm at the Coeliac axis Femoral Pseudoaneurysm
T12 level. It is a short vessel that passes
underneath the median arcuate ligament,
and then courses anteriorly or slightly
anterolaterally in the lesser sac. It is
surrounded by celiac lymph nodes and the
celiac plexus. At the upper border of the Splenic
pancreas, it divides into three branches: left artery
gastric, splenic, and common hepatic
arteries.
Common
hepatic
artery (with
aneurysm)
Common hepatic aneurysm as
incidental finding in this patient.
This is rather rare, and may be
associated with connective tissue
(e.g. Marfan syndrome) or
rheumatological disease (e.g
polyarteritis nodosum (PAN)). They
may rupture, and treatment option
is open bypass or endovascular
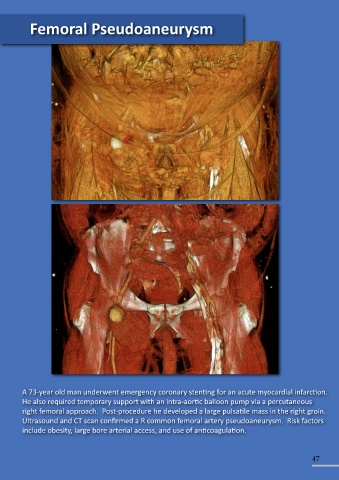
stenting/ embolization. A 73-year old man underwent emergency coronary stenting for an acute myocardial infarction.
He also required temporary support with an intra-aortic balloon pump via a percutaneous
right femoral approach. Post-procedure he developed a large pulsatile mass in the right groin.
Ultrasound and CT scan confirmed a R common femoral artery pseudoaneurysm. Risk factors
include obesity, large bore arterial access, and use of anticoagulation.
47