Page 77 - Virtual Vascular Vol 8
P. 77
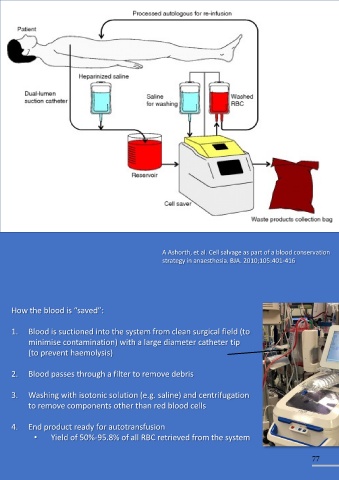
Examples of cell salvage system (“cell saver”) A Ashorth, et al. Cell salvage as part of a blood conservation
strategy in anaesthesia. BJA. 2010;105:401-416
Problems with massive allogenic blood transfusion:
• Risk of transfusion reactions and transfusion related infection
• Acidosis How the blood is “saved”:
• Hypothermia
• Coagulopathy 1. Blood is suctioned into the system from clean surgical field (to
• Electrolytes disturbance minimise contamination) with a large diameter catheter tip
• Citrate toxicity (to prevent haemolysis)
• Transfusion related acute lung injury
2. Blood passes through a filter to remove debris
Benefits of using cell savers:
• Reduce risks of transfusion 3. Washing with isotonic solution (e.g. saline) and centrifugation
• Reduce reliance on blood donation to remove components other than red blood cells
• Suitable in patients with multiple antibodies in blood or with rare blood types
• May be applicable to patients who refuses allogenic blood transfusion (e.g. 4. End product ready for autotransfusion
Jehovah’s witness) • Yield of 50%-95.8% of all RBC retrieved from the system
76 77