Page 22 - Virtual Vascular Vol 8
P. 22
Pulmonary Embolism
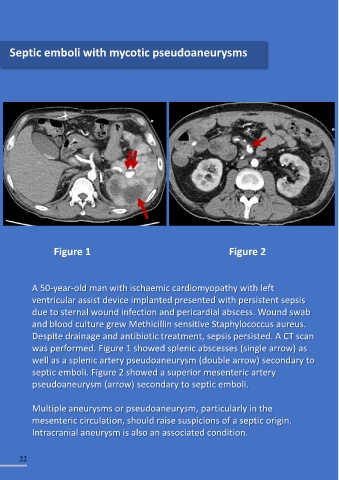
Septic emboli with mycotic pseudoaneurysms
A patient was admitted with
extensive deep vein thrombosis
involving the left lower limb. He
also presented with severe
shortness of breath and chest
pain associated with sinus
tachycardia
Figure 1
This is the CT scan finding: Serial
scan from Figure 1 to Figure 3
show massive pulmonary
embolism involving the right
pulmonary artery (arrow)
Figure 1 Figure 2
Apart from systemic
A 50-year-old man with ischaemic cardiomyopathy with left anticoagulation, in
ventricular assist device implanted presented with persistent sepsis haemodynamically unstable
due to sternal wound infection and pericardial abscess. Wound swab Figure 2 patients with massive pulmonary
and blood culture grew Methicillin sensitive Staphylococcus aureus. embolism, active intervention
Despite drainage and antibiotic treatment, sepsis persisted. A CT scan with open pulmonary
was performed. Figure 1 showed splenic abscesses (single arrow) as embolectomy, systemic
well as a splenic artery pseudoaneurysm (double arrow) secondary to thrombolysis or catheter-
septic emboli. Figure 2 showed a superior mesenteric artery directed thrombolysis/
pseudoaneurysm (arrow) secondary to septic emboli. thrombectomy should also be
considered
Multiple aneurysms or pseudoaneurysm, particularly in the
mesenteric circulation, should raise suspicions of a septic origin.
Intracranial aneurysm is also an associated condition.
22 23
Figure 3